谷口研究室 Taniguchi Lab
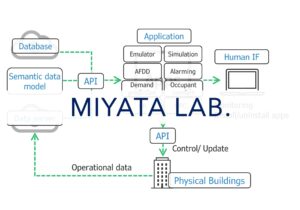
様々な技術の発展に伴い、建築物の形態は多様化し、外皮デザインは複雑化し、そして設備システムは高度化しています。そのような状況の変化の中で省エネルギーかつ快適な建築物を実現させるためには、設計時の環境シミュレーションによる高精度な予測と運用時のデータセンシングによるマネジメントが不可欠です。
谷口研究室では、環境シミュレーション・IoT技術を用いた建築設計・運用手法の提案と実践を主要なテーマに掲げて、次のような研究活動を進めています。
With the development of various technologies, building forms are diversifying, envelope designs are becoming more complex, and equipment systems are becoming more sophisticated. In order to realize energy-saving and comfortable buildings under such changing circumstances, highly accurate prediction by environmental simulation during design and management by data sensing during operation is indispensable.
Taniguchi Lab. is promoting the following research activities under the main theme of proposing and implementing architectural design and operation methods using environmental simulation and IoT technology.
Taniguchi Lab. is promoting the following research activities under the main theme of proposing and implementing architectural design and operation methods using environmental simulation and IoT technology.
1) デジタルツインを活用した個人差対応型環境制御システムの構築
1) Construction of an environmental control system that responds to individual differences by utilizing a digital twin.
建築空間には温度や気流、照度といった環境要素の分布(ムラ)が必ず存在します。また、人間の温冷感も個人の嗜好や行動の履歴によって様々です。
そこで、より多くの在室者にとってより快適性の高い空間の実現を目指して、空間環境分布を環境シミュレーションやセンシングさらには機械学習を用いて把握し、個人の温冷感特性とのマッチングをおこなう情報提供システムや空調制御システムを開発します。
そこで、より多くの在室者にとってより快適性の高い空間の実現を目指して、空間環境分布を環境シミュレーションやセンシングさらには機械学習を用いて把握し、個人の温冷感特性とのマッチングをおこなう情報提供システムや空調制御システムを開発します。
In architectural spaces, there is always a distribution (unevenness) of environmental elements such as temperature, airflow, and illumination. In addition, human perception of temperature and cooling also varies depending on personal preferences and behavioral history.
To realize more comfortable spaces for as many occupants as possible, we are developing information provision systems and air conditioning control systems that use environmental simulation, sensing, and machine learning to understand the spatial environmental distribution and match it with individual temperature and cooling sensation characteristics.
To realize more comfortable spaces for as many occupants as possible, we are developing information provision systems and air conditioning control systems that use environmental simulation, sensing, and machine learning to understand the spatial environmental distribution and match it with individual temperature and cooling sensation characteristics.
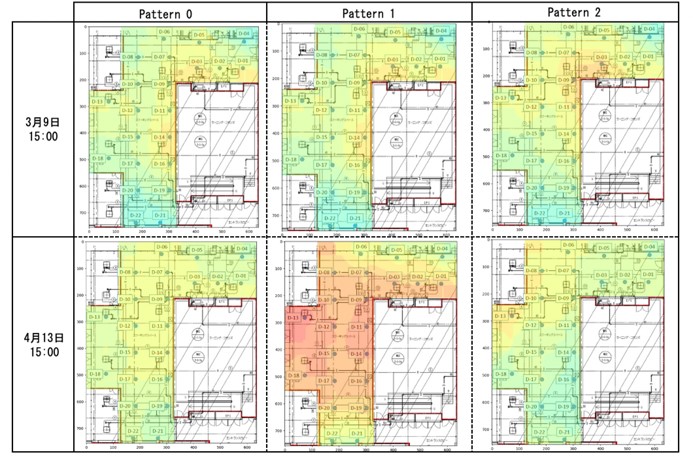
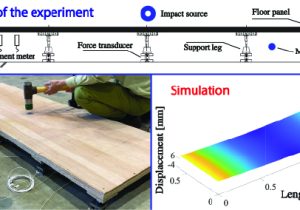
2) 平常時のセンシングによる建築設備のリスク評価・診断手法の開発
2) Development of risk assessment and diagnosis method for building facilities by sensing under normal conditions
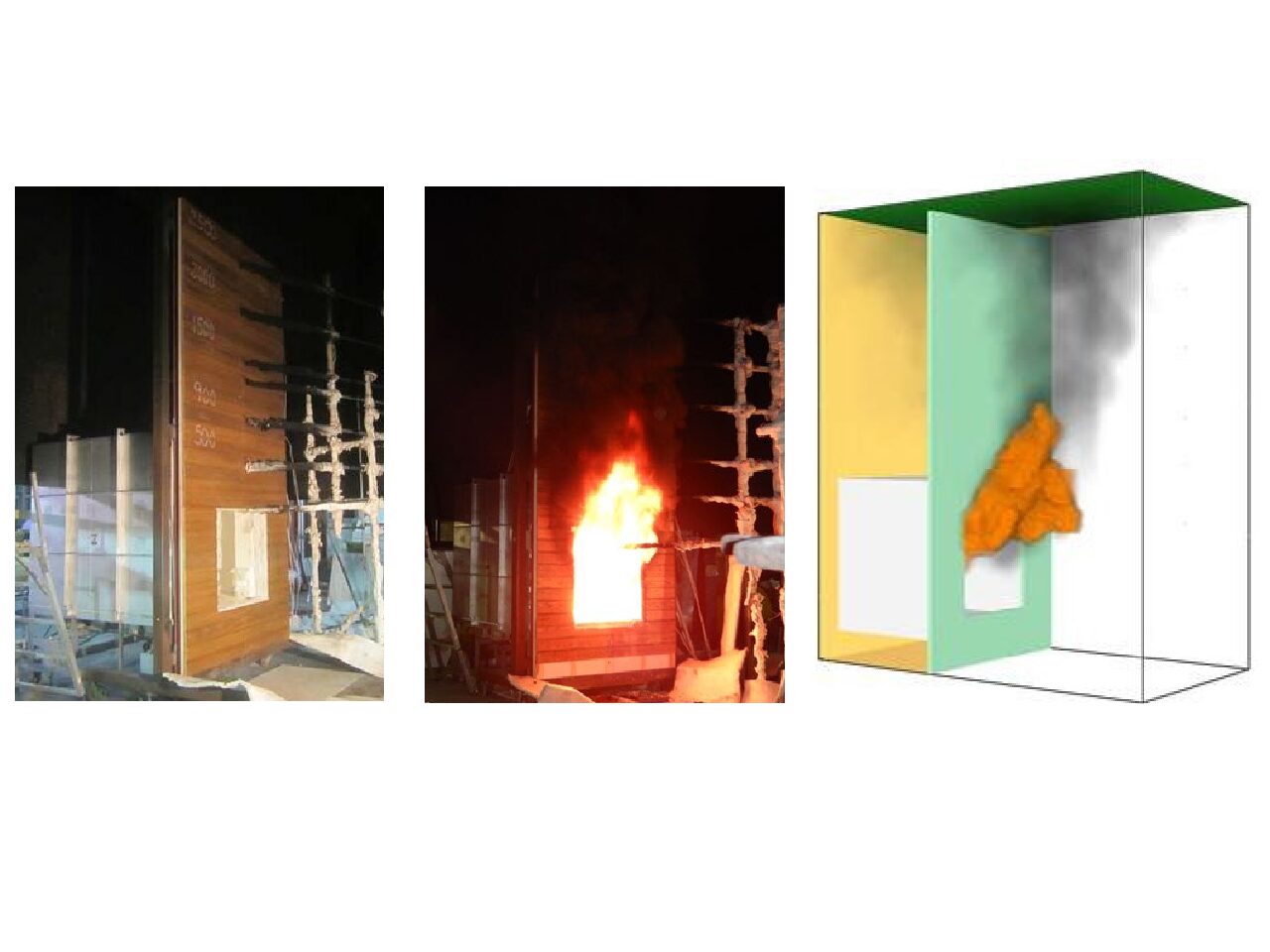
空調・設備といった建築設備は、間仕切りなどのプランニングや人員密度の変化、設備の経年劣化などの“不確かさ”の要素に起因して運用の実態は必ずしも設計時の予測通りとはなりません。設備の日々の運用状況をセンサーによってモニタリングすることは、運用の実態を正しく把握するだけでなく、地震などの災害時のリスク評価・復旧予測を正確に行うことにもつながります。
日々の運用改善と災害時のリスク予測を両立させることを目指した、データドリブンな建築設備のリスク評価・診断手法を提案します。
日々の運用改善と災害時のリスク予測を両立させることを目指した、データドリブンな建築設備のリスク評価・診断手法を提案します。
The actual operation of building facilities, such as air conditioning and equipment, does not always match the predictions made at the time of design due to “uncertainty” factors such as planning of partitions, changes in personnel density, and age-related deterioration of equipment. Monitoring the daily operational status of facilities using sensors not only provides an accurate understanding of the actual status of operations but also leads to accurate risk assessment and recovery prediction in the event of disasters such as earthquakes.
We propose a data-driven risk assessment and diagnosis method for building facilities that aim to both improve daily operations and predict risks in the event of a disaster.
We propose a data-driven risk assessment and diagnosis method for building facilities that aim to both improve daily operations and predict risks in the event of a disaster.
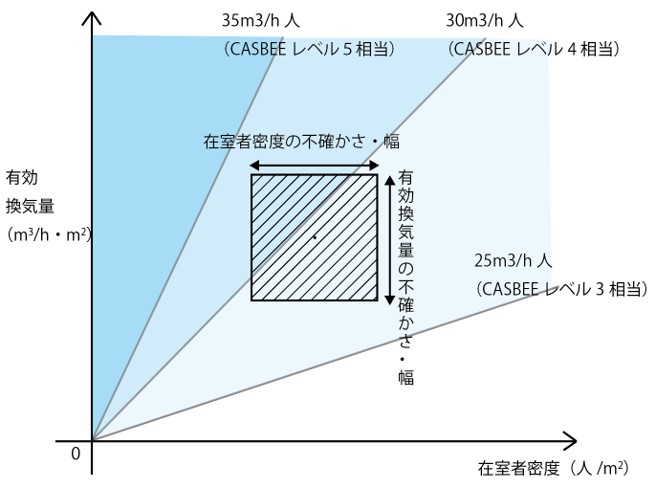
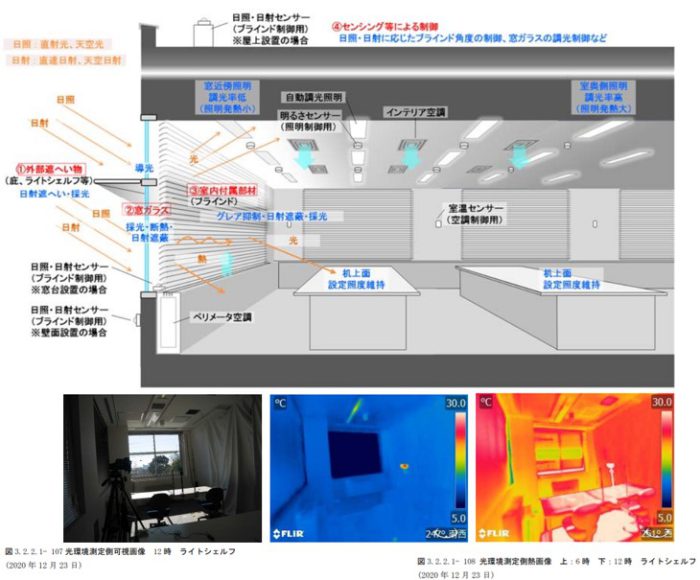
3) 窓・開口部が省エネルギー性・快適性に与える影響の総合評価手法の提案
3) Proposal for a comprehensive evaluation method of the impact of windows and openings on energy efficiency and comfort
建築物において窓・開口部は省エネルギー性・快適性に大きな影響を与える要素の1つです。また、意匠性にも大きく関わるとともに、眺望性やプライバシー性など様々な評価指標が複合的に関係します。
設計時の有効活用を想定した、建築外皮と空調・照明設備との一体的なエネルギー消費性能などの総合的な評価手法を検討します。
設計時の有効活用を想定した、建築外皮と空調・照明設備との一体的なエネルギー消費性能などの総合的な評価手法を検討します。
In buildings, windows and openings are one of the elements that have a significant impact on energy conservation and comfort. In addition, they are also greatly related to design, and various evaluation indicators, such as viewability and privacy, are related in a complex manner.
We examine comprehensive evaluation methods such as integrated energy consumption performance of the building envelope, air conditioning, and lighting equipment, assuming effective utilization at the time of design.
We examine comprehensive evaluation methods such as integrated energy consumption performance of the building envelope, air conditioning, and lighting equipment, assuming effective utilization at the time of design.
本研究室では、環境シミュレーションや機械学習など新しくコンピュテーショナルな技術を習得する意欲のある学生の方を歓迎します。
We welcome students who are willing to learn new computational techniques such as environmental simulation and machine learning.